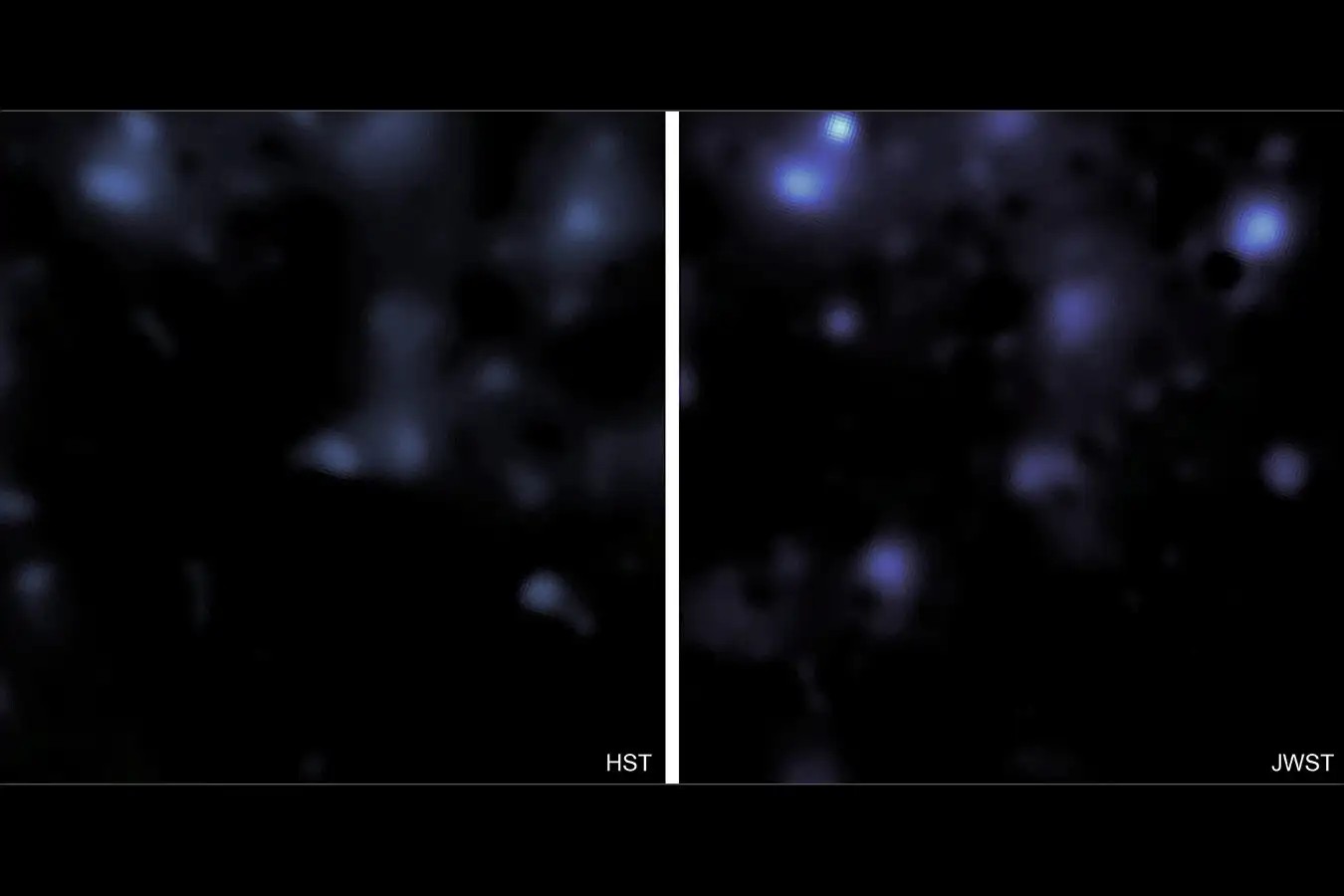
Scientists have unveiled the most detailed map of dark matter to date, leveraging the power of the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) to observe subtle distortions in the light from roughly 250,000 galaxies. This breakthrough offers unprecedented insight into one of the universe’s greatest mysteries: the nature and distribution of dark matter.
The Invisible Universe
Dark matter itself does not interact with light, making it impossible to observe directly. Instead, researchers rely on its gravitational effects, which warp the fabric of space-time and bend the path of light passing through it. This phenomenon, called gravitational lensing, allows scientists to infer the presence and density of dark matter by analyzing the distorted shapes of distant galaxies.
The JWST’s high-resolution capabilities have enabled a map with twice the clarity of previous efforts, revealing structures that were previously hidden from view. The analyzed region of sky, though slightly larger than the full moon, contains massive clusters of galaxies and the connecting filaments of the cosmic web – a large-scale structure believed to hold the universe together.
Unexpected Discoveries
The map reveals that some dark matter structures don’t align with those made of ordinary matter, indicating regions dominated by dark matter alone. This finding is significant because dark matter constitutes about 85% of all matter in the universe, and understanding its distribution is crucial for modeling the evolution of galaxies, clusters, and the cosmos as a whole.
“To identify many of these structures over a wide field, gravitational lensing is one of very, very few techniques, and definitely the best.” – Liliya Williams, University of Minnesota
Implications for Cosmology
The new dark matter map aligns with the current standard model of the universe (lambda-CDM), but researchers are conducting further analysis to explore potential discrepancies. Such investigations could refine our understanding of cosmological parameters, including the strength of dark energy—the mysterious force driving the accelerating expansion of the universe.
This observational breakthrough promises a wealth of future insights, enabling more accurate cosmological modeling and a deeper understanding of how galaxies form and evolve within their dark matter halos. While initial results confirm existing theories, the full implications of this high-resolution map remain to be uncovered.